St. James's Park is a 23 hectare (58 acre) park in Westminster, central London, the oldest of the Royal Parks of London. The park lies at the Southernmost tip of the St. James's area, which was named after a leper hospital dedicated to St. James the Less.

St. James's Park is bounded by Buckingham Palace to the West, The Mall and St. James's Palace to the North, Horse Guards to the East, and Birdcage Walk to the South. The park has a small lake, St. James's Park Lake, with two islands, Duck Island (named for the lake's collection of waterfowl), and West Island. A bridge across the lake affords a Westward view of Buckingham Palace framed by trees and fountains, and a view of the main building of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, similarly framed, to the East.
The park is the most easterly of a near-continuous chain of parks that also comprise (moving Westward) Green Park, Hyde Park and Kensington Gardens. The closest London Underground stations are St. James's Park, Victoria, and Westminster.
History[]
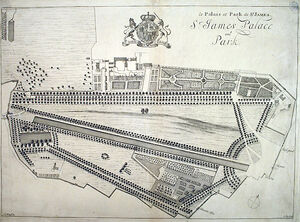
André Mollet's design for the park in Charles II's time, before 18th and 19th century remodelling, which shaped a more natural-looking lake from the straight canal visible here, the eastern part of which was filled in to create Horse Guards Parade.
In 1532, Henry VIII purchased the area of swampy marshland, often flooded by the Tyburn, from Eton College. This land lay to the West of York Palace (afterwards renamed Whitehall), recently acquired by Henry from Cardinal Wolsey; it was purchased in order to turn York Palace into a dwelling fit for a King. On James I's accession to the throne in 1603, he ordered the park drained and landscaped, and kept various exotic animals in the park, including camels, crocodiles, and an elephant, as well as aviaries of exotic birds along the south.
During Charles II's exile in France under the Commonwealth of England, the young king was impressed by the elaborate gardens at French royal palaces, and on his ascension had the park redesigned in a more formal style, probably by the French landscaper André Mollet. This included the creation of the 775 by 38 metre (850 by 42 yard) canal visible in the old plan shown to the right. Charles II opened the park to the public, as well as using the area to entertain guests and mistresses, such as Nell Gwyn. The park was notorious at the time as a meeting place for acts of degeneracy, of which John Wilmot, 2nd Earl of Rochester wrote in his poem A Ramble in St. James's Park.
The 18th century saw further changes, including the reclamation of part of the canal for Horse Guards Parade and the 1761 purchase of Buckingham House (now Buckingham Palace) by the Royal Family.

Green Park and St. James's Park c.1833
Further remodelling in 1826–7, commissioned by the Prince Regent (later George IV) and overseen by the architect and landscaper John Nash, saw the straight canal's conversion to a more naturally-shaped lake, and formal avenues be rerouted to more romantic winding pathways. At the same time, Buckingham House was expanded to create the current palace and Marble Arch was built at its entrance, whilst The Mall was turned into a grand processional route, opened to public traffic 60 years later in 1887, the Marble Arch having been moved to its current location at the junction of Oxford Street and Park Lane in 1851 and replaced with the Victoria Memorial between 1906 and 1924.
External links[]
Royal Parks [1]
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). That Wikipedia page probably contains more information. |